How To Put In Eye Conformer
Original article
peer-reviewed
Eye Conformers as Socket Expanders in Children: Experience at a Tertiary Eye Hospital in Cardinal Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Purpose
To share our experience with pediatric orbital expansion using eye conformers for anophthalmia and microphthalmia and parental feedback on outcomes.
Methods
Cases of congenital anophthalmia and severe microphthalmia were managed with center conformers for orbital expansion and germination of lid fornices at the anaplastology dispensary of King Khaled Middle Specialist Infirmary, Kingdom of saudi arabia. Data were collected on the globe adaptation procedure and the perceived achievements by the parents at different follow-upwards visits. Parental feedback was collected on their acceptance of middle conformer use to address anophthalmia and microphthalmia.
Results
The anophthalmia/microphthalmia annual prevalence was 1.vii per 10,000 live births in Saudi Arabia. Of the 45 sockets treated for orbital expansion since 2014, 15 children were managed by using eye conformers. Six children had a bilateral nascency defect. Severe microphthalmia was in seven children while eight children had anophthalmos. At the first visit, small heart conformers (ix), stem centre conformer (4), symblepharon ring (one), and hydrogel eye conformer (one) were fitted. After multiple visits and follow-ups, at the two-twelvemonth follow-up, seven (46.vii%) children were fitted while three (20%) were under the process of prosthesis fitting, as volume expansion was satisfactory. Parents of these children replied that they adopt this method over others and would recommend others to follow the same.
Conclusions
Orbital expansion and lid fornices formation past using an centre conformer is effective, piece of cake, and adequate to parents. Information technology can exist initiated in the early on months of a child's life.
Introduction
Built anophthalmia and microphthalmia are rare diseases that crusade anomalous orbitofacial growth and significant visual morbidity. Built anophthalmia is the consummate absence of the eye due to malformation of the optic vesicle during early gestation [1]. Microphthalmia is the presence of a hypoplastic or rudimentary eye at nascence [1]. The prevalence of built anophthalmia and microphthalmia ranges from 0.2 to three.0 per x,000 births [two].
The absence of a normal-sized globe is associated with orbital os and soft tissue retardation and hemifacial microsomia. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans enable clinicians to dominion out associated neurological, renal, cardiac, or other defects [3]. The direction of severe microphthalmia or anophthalmia involves stimulating orbitofacial growth. Different techniques and materials take been used to expand the orbital book, including acrylic conformers, spherical orbital implants, mucous grafts, dermis fat grafts, bone and muscle grafts, inflatable balloon devices, and hydrogel expanders [4].
However, the growth of eyelids and orbital bones also crave stimulation either meantime or shortly later addressing orbital volume expansion. Hence, the rehabilitation process should begin soon after nativity. Parents often reject surgical management because their children are very young. In cases where surgical management is refused, progressive expansion therapy with custom centre conformers followed by custom ocular prostheses is a reasonable pick. Previous studies take reported that socket expansion with self-inflating expanders and custom-made centre conformers produce similar outcomes [v].
A conformer is a clear acrylic shell fitted to an anophthalmic socket or in the case of a microphthalmia socket earlier fitting an ocular prosthesis. It helps in the formation of fornices and helps expand the socket. In the case of built contracted sockets, we demand to change conformer size every six weeks to two months for size to expand the socket gradually. It is as well used after an enucleation an evisceration of the eyeball over the implant within the socket to agree the shape of the eye socket and permit the eyelids to blink over the beat out without rubbing the suture line. The conformer shell holds the shape fix for the artificial eye.
At the Rex Khaled Eye Specialist Hospital (KKESH), Saudi arabia, 3 experienced technicians at the anaplastology clinic provide centre conformer sizing, plumbing equipment, and follow-up services for children with congenital anophthalmia and microphthalmia. At that place is a relative paucity of literature on the use and outcomes of conformers for these congenital atmospheric condition. In this written report, nosotros present the management outcomes of eye conformers for pediatric anophthalmia and severe microphthalmia in relation to increasing orbital volume, offering cosmetic outlook, the stability of the prosthesis, and parental satisfaction.
Materials & Methods
This one-armed retrospective cohort written report was performed from January 2020 to June 2020. The Institutional Research Board approved this report (2031-R). Written consent was waived due to the retrospective data collection. Yet, parents of some children provided written consent to use photos for research publications and presentations while maintaining the anonymity of the children. This study adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Children with contracted sockets due to congenital anophthalmia or microphthalmia, who were managed with middle conformers at the anaplastology clinic at KKESH between 2014 and 2019 were included in this written report. Children with less than ane year of follow-up after center conformer fitting were excluded from the written report.
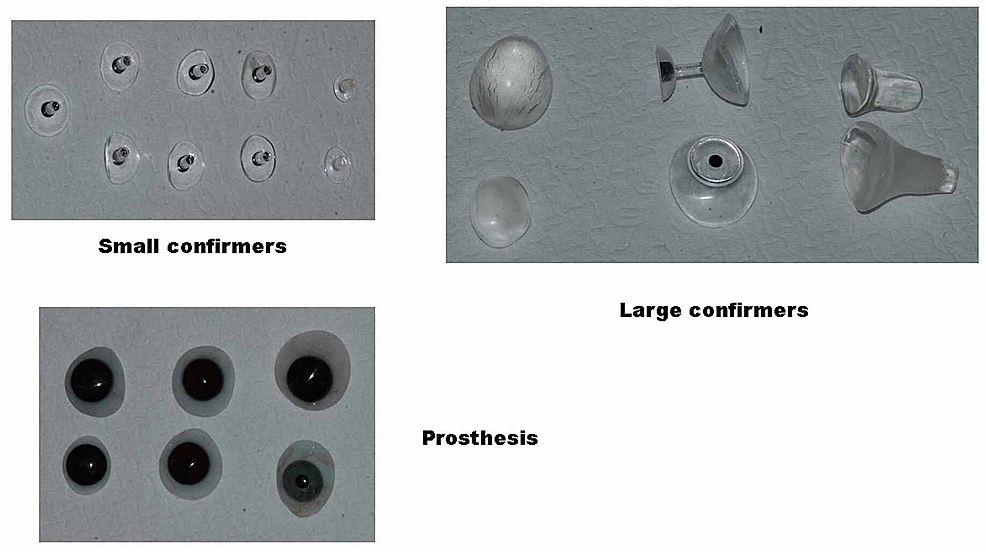
Electronic health records were used to collect data on patient demographics, the severity of the malformation, laterality (right or left eye), and other associated nativity defects, including facial asymmetry. Data were also collected on the details of the showtime eye conformer and its status at follow-up visits every six to 8 weeks in relation to extrusion, pain, crying, ulcer formation, and other signs and symptoms of adverse events. Different eye conformer sizes were used in the present study (Figure 1).
The fitting was retested every half-dozen to eight weeks, and a larger eye conformer was fitted based on the germination of the fornices, expansion of the orbit, and the loosening of the palpebral fissure.
At the two-year follow-up, a prosthesis was fitted into the orbit and measured. As nosotros enrolled a pediatric patient population, MRI or CT was non performed for measuring orbital volume. Hence, in the current report, the clarification of the fitting procedure is based on the perception of the technician reviewing photographs at different stages of heart conformer fitting, replacement, and, finally, prosthesis implantation.
The alter in orbital volume due to middle conformer fitting was defined equally the difference in book from pre-insertion to 2 years follow-upward. Success was defined as no extrusion of the prosthesis, fornices that were deep enough, and a palpebral fissure of the affected side that matched the fellow normal eye in unilateral cases. A gradual increase in heart conformer size without whatsoever complications was also considered a success.
Parental feedback was collected on satisfaction with the facial aesthetics compared to the past and whether they would recommend this choice to other parents.
The prevalence of anophthalmia and microphthalmia in relation to live births equally reported in Saudi arabia in 2019 was calculated [six]. The data were collected on a pretested class and transferred to the Statistical Package for the Social Studies for Analysis (SPSS 25, IBM Corp., Armonk, NY). Numbers and percentages are reported for chiselled variables. Median and interquartile range (IQR) are reported for continuous variables.
Results
The anaplastology clinic staff have assessed 513 sockets of 365 patients with anophthalmia or severe microphthalmia at the time of this written report. The prevalence of anophthalmia was 1.7 per 10,000 live births. Since 2014, 45 sockets have undergone volume enhancement procedures, including 22 (48.nine%) that received a polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) implant, six (13.3%) that underwent an autologous dermis fat graft, two (4.4%) that received a polyethylene implant, and fifteen (33.3%) received expanders.
The study cohort included 15 children with microphthalmia/anophthalmia treated with eye conformers for orbital expansion during the study period. The median age of the children on the day of the first visit was 375 days (IQR 190; 1170). Nine (56.3%) were boys and vii (43.7%) were girls. The youngest child was 48 days erstwhile. Six children had bilateral nascence defects while 9 children had unilateral anophthalmia. Severe microphthalmia was noted in seven children and eight children had anophthalmia.
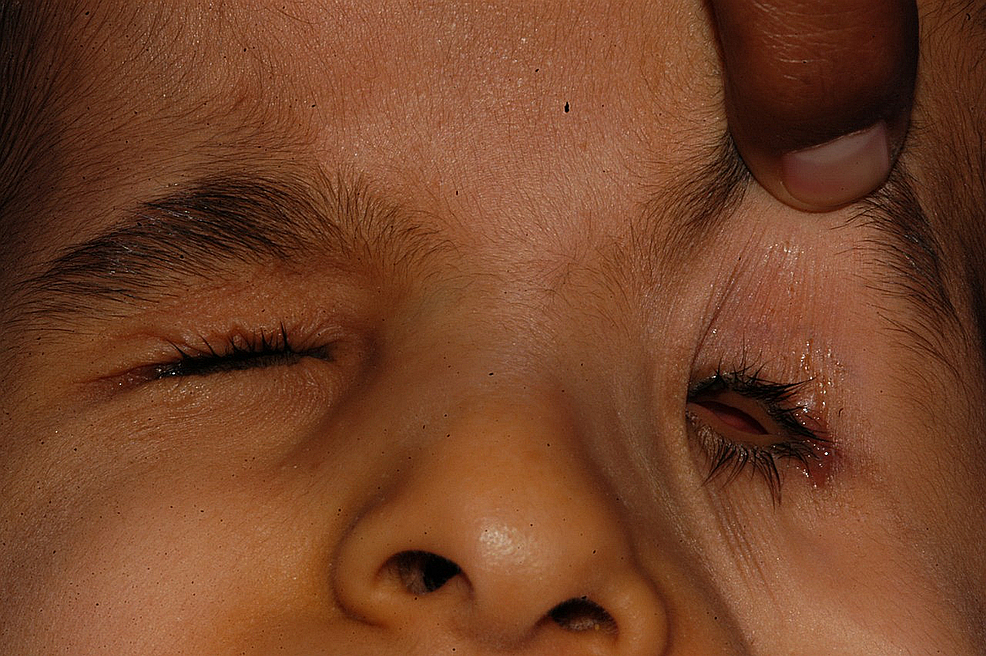
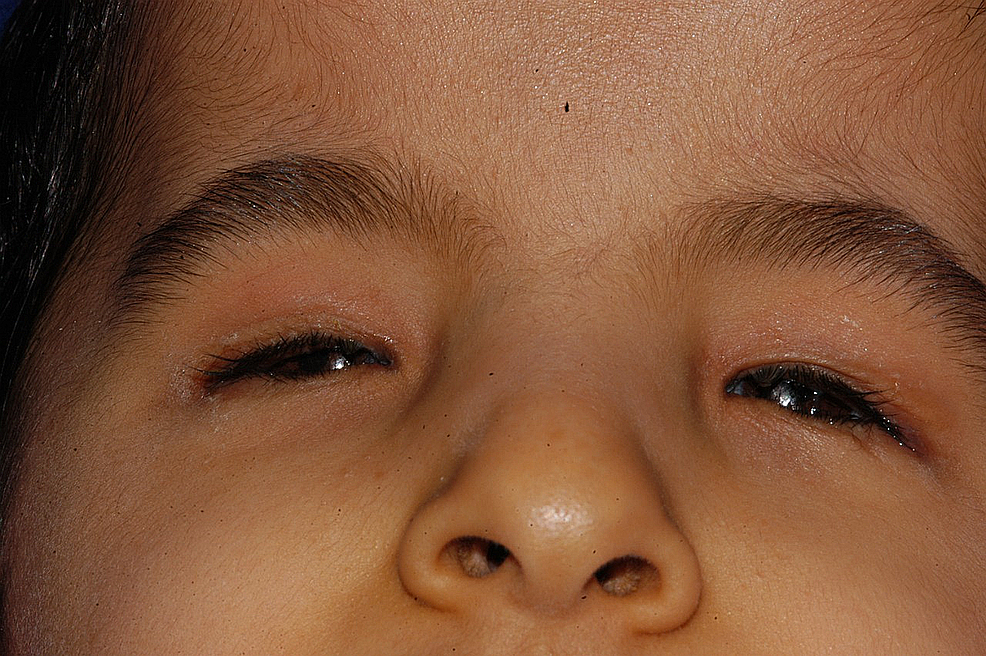
On the starting time visit, nine children were fitted with small eye conformers, of whom six received undersized centre conformers. Four children were fitted with stalk eye conformers, and ane kid each received a symblepharon band and hydrogel middle conformer. Effigy ii shows the condition of the anophthalmic orbits of a child.
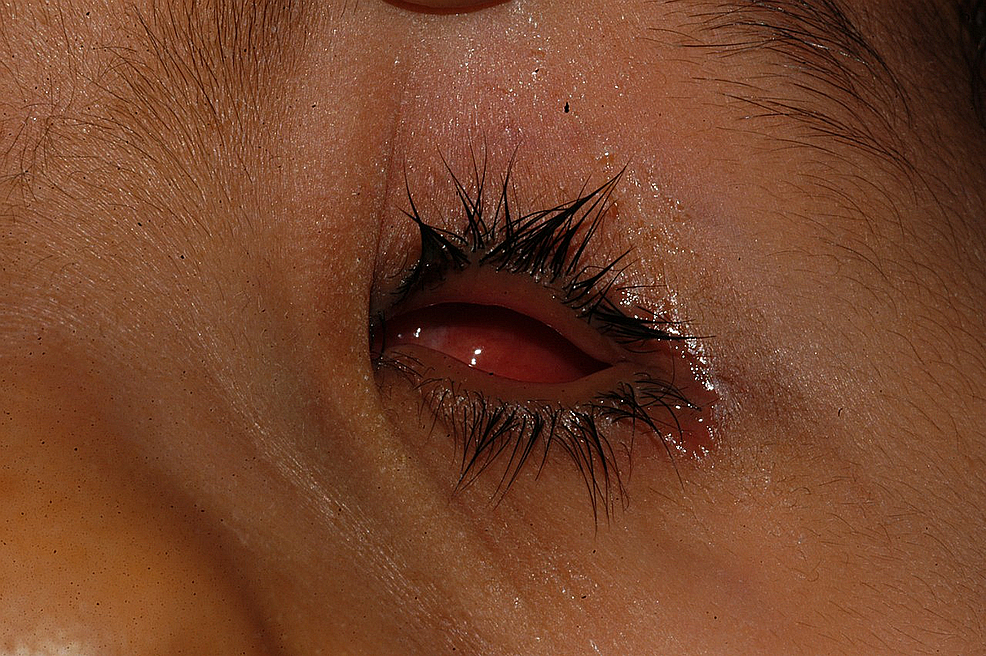
On the second visit, six to eight weeks after the first visit, small-scale middle conformers were continued for three children, six children were fitted with stem eye conformers, and two children each were fitted with medium and segmental eye conformers. One child who was fitted with a symblepharon ring blazon of eye conformer was more frequently monitored but the same treatment was connected. I child failed to present for the scheduled visit. Figure 3 shows a small center conformer fitted in the right orbit of a child.
On the third visit at three to three indicate 5 (3.five) months after initial middle conformer fitting, one child continued with a pocket-size heart conformer, two had medium centre conformers, 3 had regional center conformers, and six children had large stem center conformers. One child's fitting was ongoing while two children did non nowadays for this follow-up visit.
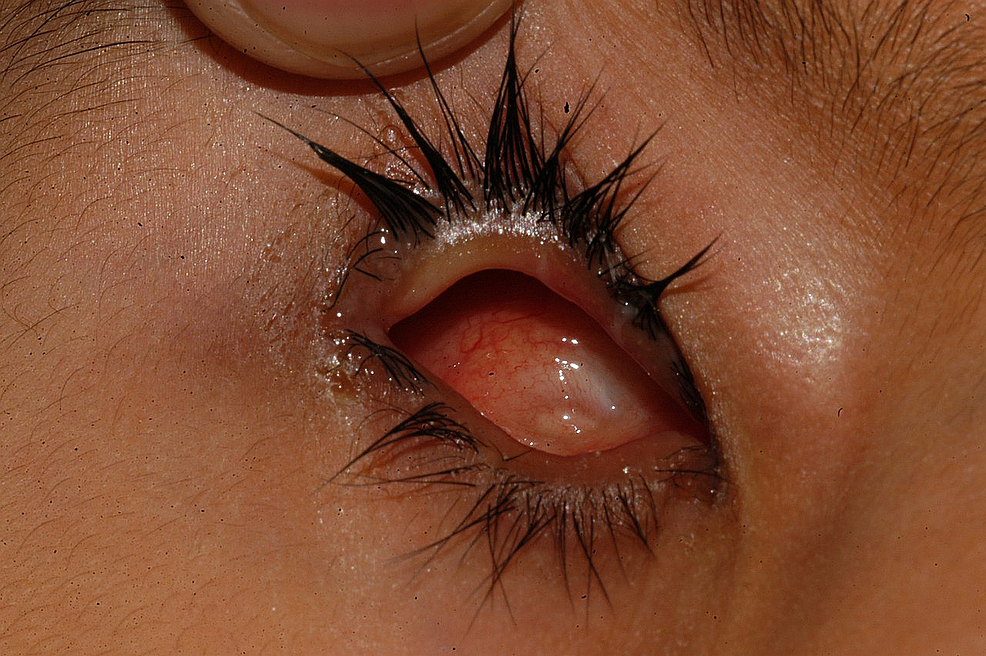
On the fourth follow-up visit, ane year after initial eye conformer plumbing fixtures, v children were provided with a prosthesis, one with a regional eye conformer, and 1 with a large centre conformer. In three children, the plumbing fixtures of the eye conformer was ongoing while 3 children were non included in the adjacent stride of treatment. Figure 4 shows the condition of the orbit and fornices on the correct side of the confront of a child after one year of confirmer fitting and increase in size gradually.
At the 5th follow-up visit, ii years after the initial conformer fitting, three more than children were fitted with a prosthesis. 1 child'due south prosthesis was increased in size. Effigy 5 shows a prosthesis fitted in both orbits after information technology was expanded with the assistance of confirmers.
If we consider the loss to follow-up that could be due to many factors, including parents non satisfied with rehabilitation, or the child'southward other ailments making them decorated in other activities, the success rate of orbital expansion was 12/15 = eighty%. At the fourth dimension of writing, seven (46.7%) of fifteen children were provided a prosthesis after volume expansion with conformers. Fitting of the conformer was ongoing in iii (20%) children. The feedback from these three children'due south parents suggested that they only prefer this method over surgeries for their children and would recommend this management to others prior to because more invasive methods.
Discussion
In this study, nosotros nowadays our experience with orbital expansion using a minimally invasive alternative that circumvented surgery on pediatric patients while achieving remarkable success. The procedure was besides child-friendly and, therefore, more acceptable to the parents. This method can stimulate the development of the fornices and lids and, therefore, maintain the prosthesis.
The prevalence of anophthalmia and microphthalmia of 1.7 per ten,000 live births is lower than that reported in Texas, Us (3/10,000), and Kingdom of denmark (3.6/10,000) [7-8]. Sixty per centum of our cases were bilateral. In a published series of five children with microphthalmia, 40% had bilateral involvement [9]. The orbital and facial growth in the get-go year of life of a kid without a globe results in pregnant facial asymmetry [10]. Irrespective of laterality, the diagnosis and management remain the same. Clauser et al have described the epidemiology, diagnosis, and management principles [11]. Yet, the apply of orbital expanders are suggested after 6 months of age in a child with a disability. Morrow et al cautioned that if the management of the orbit does not embark in infancy, good results may non be accomplished if interventions are initiated during babyhood [12]. Our method of using conformers could embark soon subsequently birth with parental consent. Hence, a thorough give-and-take of the benefits (and risks) of early intervention with the parents is fundamental to achieving practiced outcomes.
Although plastic surgeons currently recommend using hydrogel expanders, like outcomes have been reported with middle conformers [13]. In our establish, nosotros have noted complications of silicone implant in two cases of congenital anophthalmia [14]. This resulted in offering a safer and more acceptable alternative for expanding the orbit for parents who refuse surgery for their children. The dissimilar methods of orbital expansion of contracted sockets in children, along with their benefits and disadvantages, are described in Table 1.
This study has some limitations, including the lack of objective measurements to document the orbital expansion during the written report. However, eye conformer treatment began in the showtime year of life in about cases, and to mitigate needless exposure to radiations, nosotros elected not to perform imaging studies (CT and MRI) on this pediatric population.
Conclusions
Some proponents of orbital expansion and improving aesthetic outcomes for congenital anophthalmia and microphthalmia claim, with limited cases, that dermis fatty grafts or hydrogel expanders are a better option. Each i has benefits and disadvantages. Multiple surgical interventions is non favored in children of tender age and parents also do not accept the adventure of anesthesia for these procedures. But the procedure we take described to aggrandize the orbit in children with anophthalmia with severely contracted sockets is a gradual procedure to expand, does non require surgery, is less painful to the child, and offers similar cosmetic results. It is less expensive and with minimum side effects of material existence inserted in the orbital socket. Therefore, we described the procedure performed in our plant for others to understand and follow. We are not postulating that conformers are the best pick but rather, they are an acceptable alternative to service providers and to parents due to the reversibility and possibly the greater comfort for pediatric patients.
References
- Shah SP, Taylor AE, Sowden JC, et al.: Anophthalmos, microphthalmos, and typical coloboma in the Britain: a prospective study of incidence and risk. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011, 52:558-564. 10.1167/iovs.10-5263
- Shaw GM, Carmichael SL, Yang W, Harris JA, Finnell RH, Lammer EJ: Epidemiologic characteristics of anophthalmia and bilateral microphthalmia among 2.v million births in California, 1989-1997. Am J Med Genet A. 2005, 137:36-40. 10.1002/ajmg.a.30840
- Koc G, Doganay S, Ciraci S, Dogan MS, Karakukcu M, Evereklioglu C, Coskun A: Imaging evaluation of pediatric orbital pathologies. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2017, 29:525-530.
- Bernardino CR: Congenital anophthalmia: a review of dealing with book. Middle Eastward Afr J Ophthalmol. 2010, 17:156. x.4103/0974-9233.63082
- Aggarwal H, Kumar P, Singh RD: Prosthetic direction of built anophthalmia-microphthalmia patient. Arch Med Wellness Sci. 2015, three:117-126. 10.4103/2321-4848.154961
- Ministry of Health, Saudi arabia: Almanac Statistical Book. Saudi Arabia; 2018.
- Chambers TM, Agopian AJ, Lewis RA, et al.: Epidemiology of anophthalmia and microphthalmia: prevalence and patterns in Texas, 1999-2009. Am J Med Genet A. 2018, 176:1810-1818. 10.1002/ajmg.a.40352
- Roos L, Jensen H, Grønskov G, Holst R, Tümer Z: Congenital microphthalmia, anophthalmia and coloboma amidst live births in Kingdom of denmark. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2016, 23:324-330. ten.1080/09286586.2016.1213859
- Lee JS, Lee JE, Shin YG, Choi HY, Oum BS, Kim HJ: V cases of microphthalmia with other ocular malformations. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2001, xv:41-47. 10.3341/kjo.2001.xv.1.41
- Ragge NK, Subak-Sharpe ID, Collin JR: A practical guide to the management of anophthalmia and microphthalmia. Center. 2007, 21:1290-1300. 10.1038/sj.eye.6702858
- Clauser L, Sarti E, Dallera V, Galiè M: Integrated reconstructive strategies for treating the anophthalmic orbit. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2004, 32:279-290. x.1016/j.jcms.2004.04.010
- Morrow BT, Albright WB, Neves RI, Wilkinson MJ, Samson TD: Orbital expansion for congenital anophthalmia may be achievable in infancy but not in childhood. J Craniofac Surg. 2016, 27:1642-1646. ten.1097/SCS.0000000000002937
- Quaranta-Leoni FM: Built anophthalmia: current concepts in management. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2011, 22:380-384. 10.1097/ICU.0b013e328349948a
- Galindo-Ferreiro A, AlGhafri 50, Elkhamary SM, Maktabi A, Gálvez-Ruiz A, Galindo-Alonso J, Proff SS: Chronic inflammation in an anophthalmic socket due to a room temperature vulcanized silicone implant. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2016, 7:216-222. 10.1159/000445496
Original article
peer-reviewed
Eye Conformers as Socket Expanders in Children: Experience at a Tertiary Eye Hospital in Key Saudi arabia
Ideals Argument and Conflict of Interest Disclosures
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this report. Rex Khaled Center Specialist Infirmary issued approval 2031-R. Animal subjects: All authors take confirmed that this study did not involve beast subjects or tissue. Conflicts of involvement: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure class, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors take declared that no fiscal support was received from any arrangement for the submitted piece of work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or inside the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors accept alleged that at that place are no other relationships or activities that could appear to take influenced the submitted work.
Article Information
DOI
10.7759/cureus.13465
Cite this article equally:
Changal N, Khandekar R B (February 21, 2021) Eye Conformers every bit Socket Expanders in Children: Experience at a Tertiary Eye Infirmary in Cardinal Saudi Arabia. Cureus thirteen(two): e13465. doi:10.7759/cureus.13465
Publication history
Peer review began: December 24, 2020
Peer review concluded: February 14, 2021
Published: February 21, 2021
Copyright
© Copyright 2021
Changal et al. This is an open access commodity distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License CC-Past 4.0., which permits unrestricted utilise, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
License
This is an open admission commodity distributed under the terms of the Artistic Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Original commodity
peer-reviewed
Eye Conformers as Socket Expanders in Children: Experience at a Tertiary Eye Hospital in Central Saudi arabia
Figures etc.
Source: https://www.cureus.com/articles/47649-eye-conformers-as-socket-expanders-in-children-experience-at-a-tertiary-eye-hospital-in-central-saudi-arabia


0 Response to "How To Put In Eye Conformer"
Post a Comment